|
ATSDR
ToxFAQs
benzene
CAS=71-43-2
Names & Synonyms
Name of Substance
Superlist Name
- Benzene
- Benzene (including benzene from gasoline)
- Benzene [UN1114] [Flammable liquid]
- Benzol diluent
- RCRA waste no. U109
- UN1114
Synonyms
- (6)Annulene
- AI3-00808
- Benzeen [Dutch]
- Benzen [Polish]
- Benzene
- Benzene (ACGIH:OSHA)
- Benzin
- Benzin (Obs.)
- Benzine
- Benzine (Obs.)
- Benzol
- Benzol (OSHA)
- Benzol 90
- Benzole
- Benzolene
- Benzolo [Italian]
- Bicarburet of hydrogen
- CCRIS 70
- Carbon oil
- Caswell No. 077
- Coal naphtha
- Cyclohexatriene
- EINECS 200-753-7
- EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 008801
- Fenzen [Czech]
- HSDB 35
- Mineral naphtha
- Motor benzol
- NCI-C55276
- NSC 67315
- Nitration benzene
- Phene
- Phenyl hydride
- Polystream
- Pyrobenzol
- Pyrobenzole
- RCRA waste number U019
Systematic Name
File Locator
- AIDSLINE
- CANCERLIT
- CCRIS
- DART/ETIC
- DSL
- EINECS
- EMIC
- GENETOX
- HSDB
- IRIS
- MEDLINE
- MESH
- MESH HEADING
- RTECS
- SUPERLIST
- TOXLINE
- TRI95
- TRI96
- TRI97
- TSCAINV
Internet Locators
- ATSDR TOXFAQS
- EPA Envirofacts
- NIOSH ICSC
- NIOSH Pocket Guide
Superlist Locator
- CA65
- CAA1
- CGB
- DOT
- HPV
- IARC
- MA
- MI
- MTL
- NJ
- NTPA
- NTPT
- PA
- PAFA
- PEL
- PELS
- REL
- RQ
- S110
- TLV
- TRI
- WHMI
Other Registry Number
|
Authors: Anonymous
Source: TA:IARC monographs on the
Evaluation of the Carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans PG:93-148 YR:1982 IP:
VI:29
Abstract:
- Benzene has been tested in rats by intragastric administration and
inhalation exposure, and in mice by skin application, inhalation exposure and
subcutaneous injection; increase in the incidence of Zymbal-gland carcinomas.
Anaemia, lymphocytopenia and bone-marrow hyperplasia; lymphoid tumours. Benzene
does not induce specific gene mutations in bacterial systems or in Drosophila
melanogaster; cytogenetic abnormalities (chromosomal aberrations and sister
chromatid exchanges) in mammalian cells in vitro; micronucleus test; chromosomal
aberrations in the bone-marrow cells. Exposure to benzene may damage the testis.
Evidence from most studies in mice, rats, guinea-pigs and rabbits suggests that
benzene is not teratogenic at doses that are fetotoxic and embryolethal. (1)
Gasoline production, storage, transport, vending and combustion; (2) production
of other chemicals from benzene; and (3) indirect production of benzene (e.g.,
in coke ovens); major source of benzene emissions into water. Chronic human
exposure to benzene results in leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, anaemia or
combinations of these; blood dyscrasias; pancytopenia; aplasia of the bone
marrow. Benzene crosses the human placenta. There is a clear correlation between
exposure to benzene and the appearance of chromosomal aberrations in the bone
marrow and peripheral lymphocytes of individuals exposed to high levels of
benzene (>100 ppm); aberrations have been reported following chronic
exposures to as little as 10 ppm; Many case reports and case series have
described the association of leukaemia with exposure to benzene, either alone or
in combination with other chemicals. Most cases were acute myelogenous leukaemia;
Two follow-up studies showed high incidences of leukaemia among individuals
ascertained as cases of benzene haemopathy. A series of epidemiological studies,
both cohort and case-control, showed statistically significant associations
between leukaemia (predominantly myelogenous) and occupational exposure to
benzene and benzene-containing solvents. There is limited evidence that benzene
is carcinogenic in experimental animals. It is established that human exposure
to commercial benzene or benzene-containing mixtures can cause damage to the
haematopoietic system, including pancytopenia. The relationship between benzene
exposure and the development of acute myelogenous leukaemia has been established
in epidemiological studies. Reports linking exposure to benzene with other
malignancies were considered to be inadequate for evaluation. There is
sufficient evidence that benzene is carcinogenic to man. (SHORTENED)
CAS Registry Numbers:
-
- 71-43-2
Language: English
Entry Month: June, 1984
Year of Publication: 1982
Secondary Source ID: RISKLINE/1984060012
What
is Lindane Anyway?
Polycyclic
Aromatic Hydrocarbon
Carcinogen
Reproductive Toxin
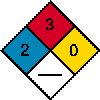
Toxic by inhalation. Liquid irritant to skin and eyes. CNS narcotic and
anaesthetic. Human carcinogen. Can damage blood components and cause severe
anaemia and bleeding.
Harmful when absorbed through the skin.
INHALATION: Cancer hazard. Can cause blood disorders. Inhalation
causes headaches, dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea, and may lead to
unconsciousness.
OTHER TOXICITY DATA: Acute toxicity of benzene results primarily
from depression of the central nervous system (CNS). Inhalation of
concentrations over 50 ppm can produce headache, lassitude, weariness,
dizziness, drowsiness, or excitation. Exposure to very high levels can result in
unconsciousness and death.
Long-term overexposure to benzene has been associated with certain types of
leukemia in humans. In addition, the International Agency for Research on Cancer
(IARC) and OSHA consider benzene to be a human carcinogen. Chronic exposures to
benzene at levels of 100 ppm and below have been reported to cause adverse blood
effects including anemia. Benzene exposure can occur by inhalation and
absorption through the skin.
Inhalation and forced feeding studies of benzene in laboratory animals have
produced a carcinogenic response in a variety of organs, including possibly
leukemia, other adverse effects on the blood, chromosomal changes and some
effects on the immune system. Exposure to benzene at levels up to 300 ppm did
not produce birth defects in animal studies; however, exposure to the higher
dosage levels (greater than 100 ppm) resulted in a reduction of body weight of
the rat pups (fetotoxicity). Changes in the testes have been observed in mice
exposed to benzene at 300 ppm, but reproductive performance was not altered in
rats exposed to benzene at the same level.
Aspiration of this product into the lungs can cause chemical pneumonia and
can be fatal. Aspiration into the lungs can occur while vomiting after ingestion
of this product. Do not siphon by mouth.
Safety Card --BENZENE 71-43-2 CY1400000
Toxic, volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon biproduct of coal
distillation. It is used as an industrial solvent in paints, varnishes, lacquer
thinners, gasoline, etc. Benzene causes central nervous system damage acutely
and bone marrow damage chronically and is carcinogenic. It was formerly used as
parasiticide.
EPA's IRIS
Benzene
Benzene Support
Documents
Vermont SIRI MSDS
Archive
RAIS Toxicity
Summary for BENZENE
Eighth
Report on Carcinogens
Amoco
Chemical -- BENZENE (AMOCO/TOTAL) CAS 71-43-2
Safety Card --BENZENE
71-43-2 CY1400000
Safety Card -- BENZOL
71-43-2 CY1400000
Safety Card --
CYCLOHEXATRIENE 71-43-2 CY1400000
Fisher
- Benzene, p.a. 71-43-2
Fisher
- Benzene 71-43-2
Fisher
- Benzene 71-43-2
Fisher
- Benzene, spectrophotometric grade 71-43-2
- [6] Annulene
- Benzine
- Benzol
- Cyclohexatriene
- Phene
Classification Code
- Agricultural Chemical
- Carcinogens
- Drug / Therapeutic Agent
- Human Data
- Mutation data
- Out-dated pesticide
- Reproductive Effect
- Skin / Eye Irritant
- Solvents
- Tumor data
Superlist Classification Code
- ATSDR Profile Priority List, rank : 5
- Known to be a carcinogen
- Overall Carcinogenic Evaluation: Group 1
- Reportable Quantity (RQ) = 10 lb
- TWA (0.5 ppm); STEL (2.5 ppm); skin; Confirmed human carcinogen
- TWA see 1910.1028; Ceiling 25 mg/m3;
ChemIDplus
|